Causes of Central Neurogenic Hyperventilation Include Which of the Following
Central neurogenic hyperventilation CNH is a rare diagnosis of exclusion characterized by hyperventilation persisting during sleep low PaCO 2 and high arterial pH. Central neurogenic hyperventilation CNH is a rare condition characterized by hyperventilation that persists even during states of sleep low PaCO2 and high arterial pH in the absence of toxic or metabolic etiologies.

Approach To The Comatose Patient Neupsy Key
Patient presentation varies based on the underlying cause and may present with a sole chief complaint of dyspnea.
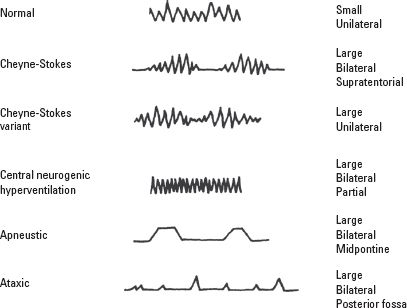
. Which of the following are causes of central neurogenic hyperventilation. Asthma Acute Chronic. Central neurogenic hyperventilation CNH for which there is no effective therapy can eventually result in respiratory fatigue and death.
Central neurogenic hypoventilation occurs when the medulla respiratory centers are not responding to appropriate stimuli. This report describes a patient with CNH due to a brainstem anaplastic astrocytoma who also exhibited disturbances of sleep and ocular motor function. The hypotonia contributes to the ataxia and intention tremor in cerebellar damage and manifests with minimal weakness and normal or slightly exaggerated reflexes.
Inadequate brain blood flow 3. 1 By definition the patient must demonstrate paraclinical evidence of hyperventilation low PaCO 2 without evidence of an underlying cardiopulmonary or toxicometabolic cause. 1 A Apneustic breathing B Biots breathing C Cheyne-Stokes breathing D Paradoxic breathing 3.
Central neurogenic hyperventilation often associated with brainstem lymphoma rare in noncomatose patients and never described in CLIPPERS results from released respiratory inhibition from medial pontine nuclear damage. Causes include CNS dysfunction cardiac failure with low cardiac output sleep hypoxia profound hypocapnia---. CNH has been described in patients with infiltrative tumors autoimmune disease and vascular lesions involving the brainstem.
Inadequate brain blood flow 3. Apneustic breathing generally occurs in the setting of pontine lesions and at last lesions in the ventrolateral medulla may cause ataxic breathing and apnea. Patients with HVS were shown to be more likely to have had overprotective parents when they were children.
Causes include pure pyramidal tract damage a rare occurrence and cerebellar damage. Central neurogenic hyperventilation CNH is a neurogenic disorder rarely described within Emergency Medicine literature. Severe brain hypoxia a.
Causes of central neurogenic hyperventilation include which of the following. Hyperventilation must occur both in. Be ruled out first.
CNH is a primary cause of hyperventilation most commonly due to primary central nervous system neoplasms. Most of the cases. 1 and 3 d.
Severe brain hypoxia 4. There are numerous causes for peripheral hyperventilation such as fever pain asthma pneumothorax pulmonary embolism drugs alcohol withdrawal ischemic heart disease and congestive heart failure hyperthyroidism5 Reported first by Plum and Swanson in 1959 central neurogenic hyperventilation. It was first described in patients exposed to acute anoxia by Plum and Swanson.
It is usually due to the midbrain and upper pons damage. Which of the following describes this patten of breathing. Treatment-emergent central sleep apnea.
However there are a few cases of hyperventilation caused by. The eyes may be involved in 20 of cases and the diagnosis may be confirmed in the appropriate setting by vitreous or aqueous aspiration. Central neurogenic hyperventilation is persistent hyperventilation typically caused by head trauma severe brain hypoxia or lack of cerebral perfusion.
True central neurogenic hyperventilation is rare and can presumably develop secondary to a lesion in the region of the parabrachial nucleus. Please Click To Know About Following Diseases. 1 2 and 3.
Being comfortably tachypneic can be. The CNH responded clinically to morphine sulfate and methadone. Predisposition to HVS may also be rooted in childhood.
1 and 2 c. The major cause of central neurogenic hyperventilation is infiltrative tumors involving the brainstem 20. Causes of central neurogenic hyperventilation include which of the following.
3CENTRAL NEUROGENIC HYPERVENTILATION. The diag-nostic criteria for CNH include hyperventilation that persists during sleep low arterial PaCO 2 high arterial PaO 2and high arterial pH in the absence of drug-induced infectious epileptic or metabolic causes. Several such stressors have been identified including emotional distress sodium lactate caffeine isoproterenol cholecystokinin and carbon dioxide.
Central neurogenic hyperventilation refers to progressive tachypnea leading to hypocarbia and respiratory alkalosis caused by cortical disorders initially reported in comatose patients with mainly pontine infarction. The term central neurogenic hyperventilation has been applied to describe the progressive tachypnea causing hypocapnia and respiratory Renal failure acute and chronic Hypoaldosteronism adrenal. 2 and 3 b.
A pure pyramidal tact injury produces hypotonia and weakness. A Cheyne-Stokes breathing pattern can occur if youre at a very high altitude. The change in oxygen at this altitude is the reason for the alternating rapid breathing hyperventilation and underbreathing.
Central neurogenic hyperventilation CNH is a rare con-dition first described by Plum and Swanson 2. First described in 1959 by Plum and Swanson CNH is a rare cause of dyspnea hypocapnea and respiratory alkalosis particularly in conscious patients. High-altitude periodic breathing.
Central neurogenic hyperventilation is often caused by CNS lymphoma. Ncbinlmnihgov Tachypnea is abnormally rapid breathing.

Respiratory Care Of The Neurosurgical Patient Anesthesia Key

Paramedic Care Principles Practice Ppt Download

Central Neurogenic Hyperventilation Neurology

Central Neurogenic Hyperventilation In A Conscious Patient With

Pdf Central Neurogenic Respiratory Failure A Challenging Diagnosis

Medical Addicts Six Types Of Abnormal Breathing 1 Kussmaul Brathing Deep Rapid Respiration With No End Expiratory Pause Causes Profound Hypocapnia Seen In Profound Metabolic Acidosis I E Diabetic Ketoacidosis 2 Cluster Breathing Groups

T2 And Flair Sequences Showing A Brain Stem Tumor Invading The Fourth Download Scientific Diagram
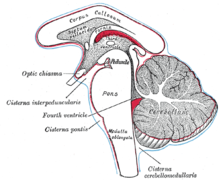
Central Neurogenic Hyperventilation Wikipedia

What Is Central Neurogenic Hyperventilation What Causes It
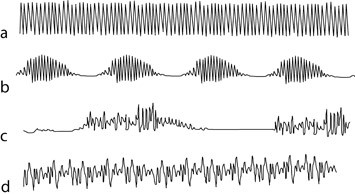
Kussmaul Respirations Springerlink

Control Of Breathing And Acute Respiratory Failure Clinical Gate

Critical Care Exam 6 Smith Flashcards Quizlet

Neurologic Control Of Respiration Flashcards Quizlet

Dr M Sofi Md Frcp London Frcpedin Frcsedin Ppt Download
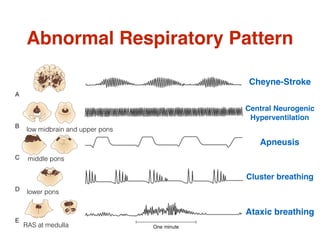



Comments
Post a Comment